
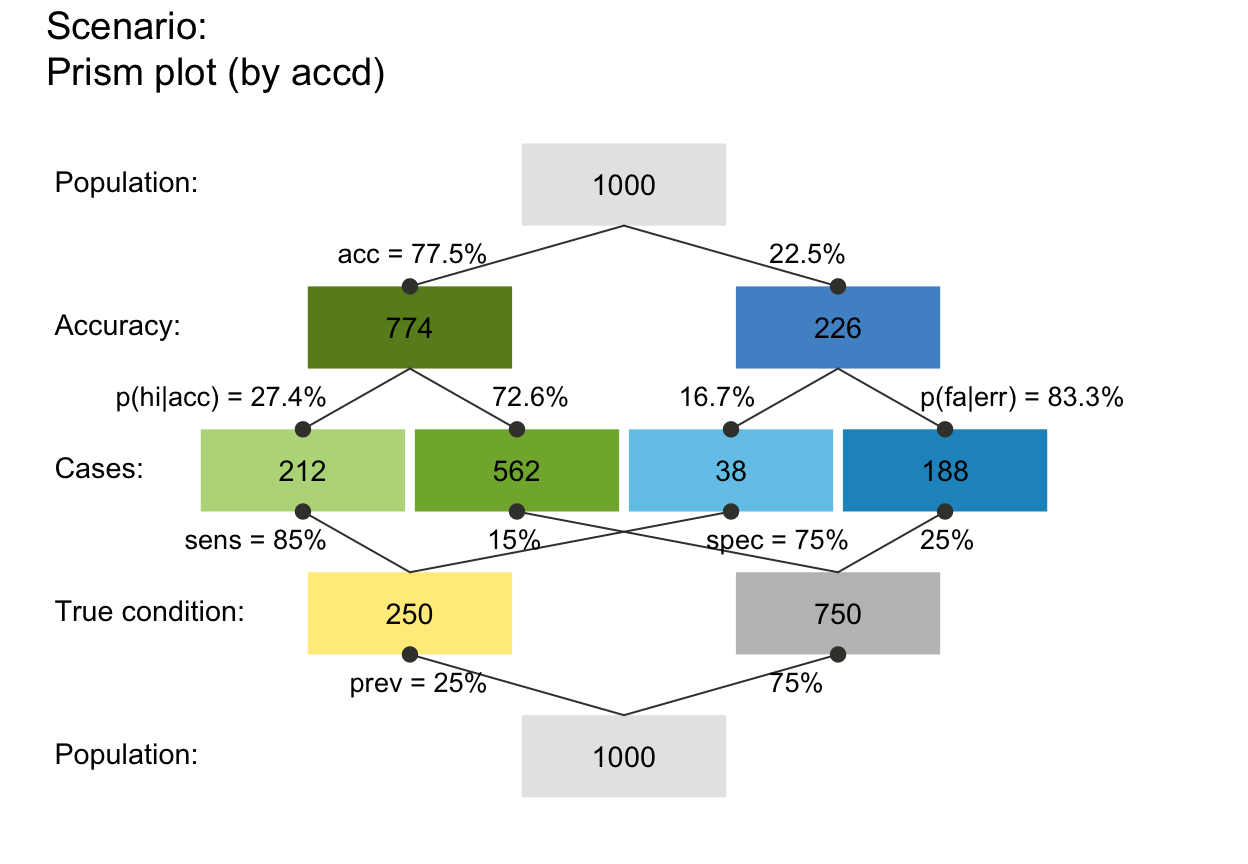
This is the default option corresponding to the methodology of Bland & Altman, 1986. ( *) or ratios when this option is selected (see below). against the sample rank (where the samples are ranked by the average of the two methods), the rank of the first method, or the rank of the second method these options will give a "Ranked order difference plot" according to CLSI, 2013.against the geometric mean of both methods.against one of the two methods, if this is a reference or "gold standard" method (Krouwer, 2008).In the original Bland-Altman plot (Bland & Altman, 1986) the differences* between the two methods are plotted against the averages of the two methods.Īlternatively, you can choose to plot the differences* You can select the following variations of the Bland-Altman plot (see Bland & Altman, 1995 Bland & Altman, 1999 Krouwer, 2008): If you have duplicate or multiple measurements per subject for each method, see Bland-Altman plot with multiple measurements per subject.
#Prism scatter plot calculator plus
Horizontal lines are drawn at the mean difference, and at the limits of agreement, which are defined as the mean difference plus and minus 1.96 times the standard deviation of the differences. Alternatively (Krouwer, 2008) the differences can be plotted against one of the two methods, if this method is a reference or "gold standard" method.
In this graphical method the differences (or alternatively the ratios) between the two techniques are plotted against the averages of the two techniques.
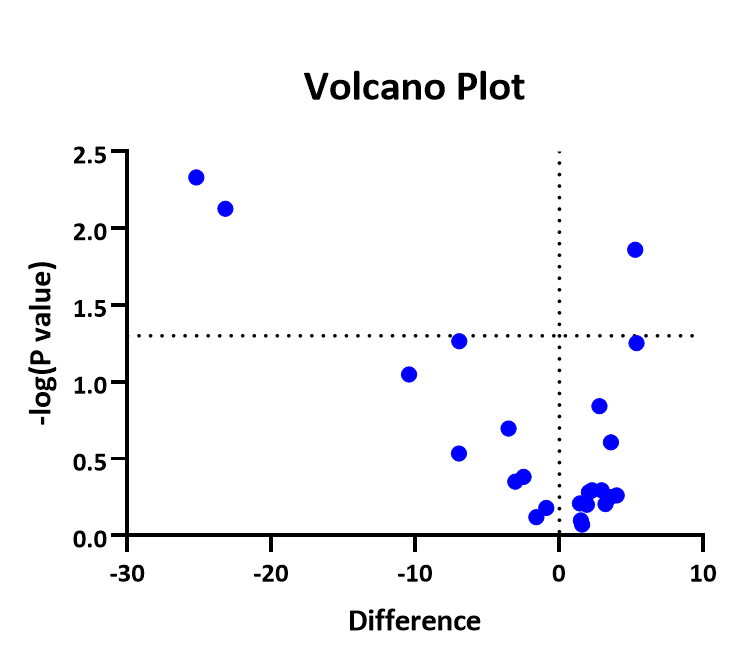
The Bland-Altman plot, or difference plot, is a graphical method to compare two measurements techniques (Bland & Altman, 19).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
